Foot fungus, a common foe for many, can be an embarrassing and irritating problem. It’s not just about the unsightly appearance; the relentless itch and burning sensation can significantly impact your daily life. But fear not! This comprehensive guide equips you with all the knowledge you need to combat foot fungus effectively.
Unveiling the Enemy: Types of Foot Fungus
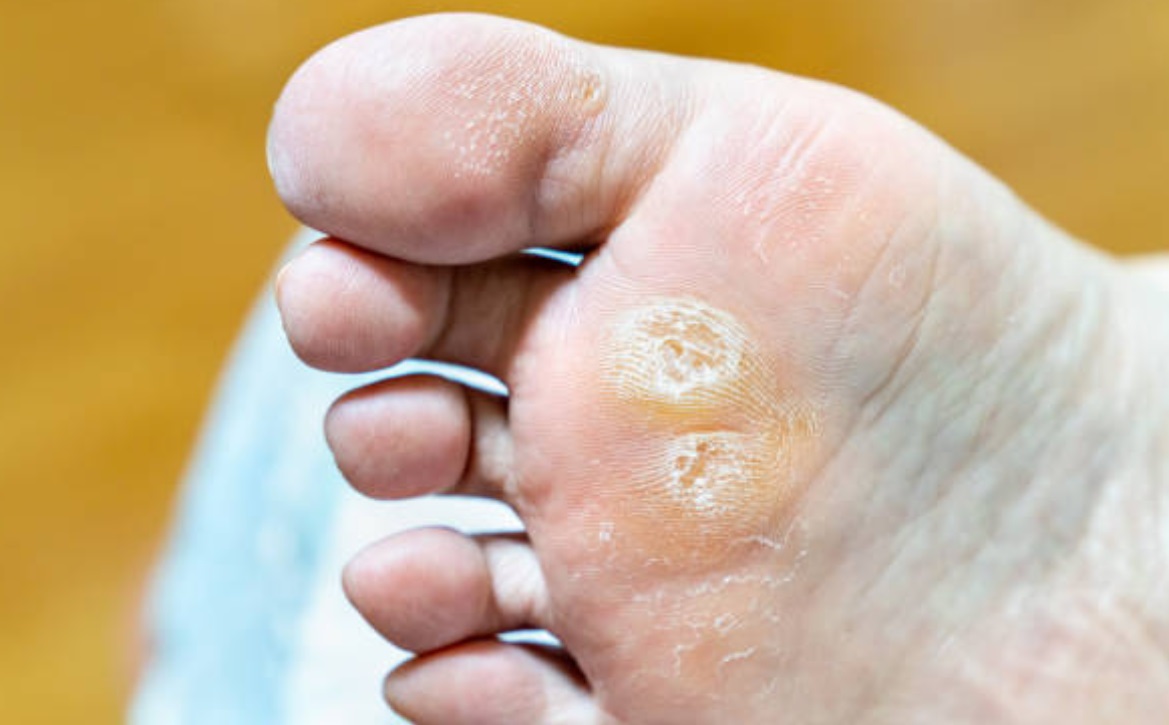
Foot fungus, medically known as tinea pedis, encompasses various fungal infections affecting different areas of the foot. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types:
- Athlete’s Foot: The most prevalent type, it thrives in warm, moist environments. Symptoms include itching, burning, scaling, and cracking of the skin between the toes, sometimes spreading to the soles.
- Moccasin Foot: This variant affects the soles and sides of the feet, causing dry, thickened, and sometimes cracked skin. It can be mistaken for eczema or dry skin.
- Vesicular Foot: This less frequent type presents with small, itchy blisters on the soles and sides of the feet. It often occurs due to prolonged exposure to damp environments.
In addition to these, fungal infections can also target the toenails, leading to a condition called onychomycosis. This causes the nails to become discolored, thickened, brittle, and even detach from the nail bed.
Digging Deeper: Causes and Risk Factors
Fungi, microscopic organisms, thrive in warm, humid environments. They can easily spread through contact with contaminated surfaces, such as:
- Shared floors in locker rooms, showers, and swimming pools
- Shoes and socks worn by someone with foot fungus
- Contaminated towels or washcloths
Certain factors can increase your susceptibility to foot fungus, including:
- Excessive sweating: Damp feet create a breeding ground for fungi.
- Tight-fitting, non-breathable shoes: These trap moisture and heat.
- Weakened immune system: Conditions like diabetes or HIV can make you more vulnerable.
- Certain medical conditions: Skin conditions like psoriasis can disrupt the skin barrier, making it easier for fungi to invade.
Recognizing the Foe: Symptoms of Foot Fungus
The signs and symptoms of foot fungus can vary depending on the type and severity of the infection. Here’s a general overview:
- Itching: This is the most common symptom, ranging from mild to severe.
- Burning sensation: The affected area may feel hot and burning.
- Scaling and cracking: The skin between the toes, soles, or sides of the feet may become dry, scaly, and develop cracks.
- Discoloration: The affected skin can appear red, white, or a brownish-yellow color.
- Blisters: In some cases, small, itchy blisters may appear on the soles or sides of the feet.
- Thickened, discolored toenails (onychomycosis): Nails may become thick, brittle, and crumble. They can also change color to white, yellow, or brown.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to seek diagnosis and treatment from a healthcare professional or dermatologist. Early intervention is key to preventing complications and ensuring a speedy recovery.
Combating the Itch: Treatment Options for Foot Fungus
The good news is that foot fungus is highly treatable with various antifungal medications. The specific treatment plan will depend on the severity and type of infection. Here are some common approaches:
- Over-the-counter (OTC) antifungal creams or sprays: These are readily available at pharmacies and are effective for mild cases. Clotrimazole, miconazole, and terbinafine are some common OTC medications.
- Prescription-strength antifungal medications: For stubborn or widespread infections, your doctor may prescribe stronger topical creams or oral medications like fluconazole or terbinafine.
- Home remedies: While not a substitute for medical treatment, some home remedies may provide some relief from symptoms. These include soaking feet in saltwater solution, applying apple cider vinegar (diluted), or using tea tree oil (always diluted with a carrier oil). However, consult your doctor before using any home remedy.
Preventing the Recurrence: Keeping Foot Fungus at Bay
Once you’ve successfully treated your foot fungus, it’s vital to implement preventive measures to prevent its return. Here are some key strategies:
- Maintain good foot hygiene: Wash your feet thoroughly with soap and water daily, especially between the toes. Dry them completely, paying particular attention to the areas between the toes.
- Wear moisture-wicking socks: Opt for cotton or wool socks that absorb moisture and allow your feet to breathe. Change your socks daily, especially if your feet sweat heavily.
- Choose breathable shoes: Avoid tight-fitting shoes and opt for well-ventilated footwear made from natural materials like leather or canvas. These allow your feet to breathe and prevent moisture buildup.
- Alternate your shoes: Don’t wear the same pair of shoes every day. This allows them to dry out completely between wearings. Consider having at least two pairs of shoes you can rotate.
- Disinfect your shoes: Regularly disinfect your shoes with antifungal sprays or powders specifically designed for this purpose. Follow the instructions on the product carefully.
- Avoid sharing personal items: Don’t share towels, socks, or shoes with others. This can easily spread foot fungus.
- Keep your feet dry: Avoid walking barefoot in public places like locker rooms or swimming pools. Wear shower shoes in these environments.
- Manage sweating: If you sweat excessively, consider using an antiperspirant spray on your feet or using foot powder to absorb moisture.
- Maintain healthy habits: A balanced diet, adequate sleep, and managing stress can all contribute to a healthy immune system, making you less susceptible to fungal infections.
- Schedule regular checkups: If you have a history of foot fungus, especially onychomycosis, it’s crucial to schedule regular checkups with your doctor or dermatologist to monitor your feet for signs of recurrence.
Bonus Tip: Targeting Toenail Fungus
Onychomycosis, the fungal infection affecting toenails, requires a more persistent approach. While topical medications can be effective in some cases, oral antifungal medications are often the preferred treatment option. These medications are typically taken for several months to ensure complete eradication of the fungus. However, it’s important to note that oral antifungals can have side effects, so it’s essential to discuss them with your doctor before starting treatment.
In severe cases, laser therapy may be an option. This non-invasive procedure uses concentrated light beams to destroy the fungus in the nail. While generally effective, laser therapy may require multiple sessions and might not be covered by insurance.
At the Conclusion: Farewell, Foot Fungus!
Foot fungus, though an unpleasant experience, is a treatable condition. By following the measures outlined in this guide, you can effectively combat the infection and prevent its return. Remember, early diagnosis and treatment are key to a speedy recovery and maintaining healthy, itch-free feet. If you have any concerns about foot fungus, don’t hesitate to consult your doctor or dermatologist for personalized advice and treatment.